$59.00
At Home Gonorrhea Test (GC STD)
Urine STD test kit with easy home sample collection. This at home gonorrhea test for men and women allows you to screen for gonococcus sexually transmitted disease (GC STD) - one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It's an ideal test if you've been notified about a potential gonorrhea exposure, or for retesting to confirm the clearance of a recent infection following treatment. Opt for this self STD check up if you're looking for easy sample collection with guaranteed privacy and rapid, accurate results.
- Detects gonorrhea
- Urine sample collection
- Same lab test offered by physicians & hospitals
- Shipped free in discreet packaging
- Upgrade – add chlamydia & trich to your urine gonorrhea test kit
$59.00
4U Health At Home Gonorrhea Test
When To Get a Gonorrhea GC STD Check
We advise waiting at least 2 weeks from the time of a potential gonorrhea exposure before undergoing a GC STD check, as it may take some time for gonorrhea to become detectable.
This GC STD check might be right for you if:
- You want to rule out gonorrhea exposure
- Become sexually active
- Engage in sexual activity
- Start a new sexual relationship
- Receive notification of gonorrhea infection from a previous partner
- You want to confirm you cleared a recent gonorrhea infection
- We recommend testing no sooner than two weeks after your completed antibiotic regimen.
- For the most accurate negative results, the CDC recommends testing at 3 months to confirm you cleared the infection and were not reinfected.1
- You are experiencing GC STD symptoms
- Pubic
- Pelvic pain
- Pain or burning during urination
- Reproductive
- Bumps, lumps, or sores around the genitals
- Discharge from the vagina or penis
- Itching or irritation on the genitals
- Pain during sex
- Painful erections
- Rash on the genitals
- Vaginal odor
- You are a parent
- If your child is sexually active, it’s a good idea to have them undergo a GC STD check
Gonorrhea Test for Men & Women: Check for One of the Most Common STIs in the U.S.
4U Health’s At Home Gonorrhea Test allows you access the same lab test that doctors and hospitals offer. From the privacy of your home, measure for gonorrhea DNA in urine. This STI is widespread in both sexes because most infected individuals don’t show any symptoms and fail to undergo preventive GC STD screening. This is a urine gonorrhea test for men and women.
- At Home Gonorrhea Test for Men & Women
- Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection most commonly seen in the genital tract. It is curable with antibiotics. This urine GC STD test can detect genital gonorrhea in both men and women.
Easily collect a urine gonorrhea test from the comfort and privacy of your own home
Your mail-in gonorrhea test kit is delivered directly to your door in discreet packaging for a confidential testing experience. Your 4U Health GC STD test kit includes everything required for your home urine sample collection. We provide detailed instructions and a prepaid shipping label to return your urine sample to the lab.

Rapid Gonorrhea Test CVS
To ensure accurate results, collect your urine sample from the first stream in the morning and return it on the same day. Please refrain from cleansing the genital area or urinating at least 1 hour before collecting your urine sample for the at home gonorrhea test for men and women.
Hospital-grade private GC STD test results
Once we receive your test, we’ll send your physician-reviewed results in approximately 2-5 days. 4U Health’s at home GC STD test report is both accurate and easy to read. Your result will tell you whether gonorrhea DNA is detected in your self-collected urine sample. If you test positive, we advise you share your GC STD status with your current and prior sexual partners so they can undergo a gonorrhea GC STD check. It’s also recommended to share your results with your doctor so they can help determine an appropriate treatment plan.
Why Test?
What's Measured?
At-Home Test Collection
Certified Lab Results
Other Online STD Tests
3 STD Check
Most Economical
Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Test
Most Economical
At Home Essential STD Test (3-STIs)
Includes Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, & Trich Urine test for gonorrhea and chlamydia
Urine Test for Gonorrhea and Chlamydia
Simple STD check for both men and women detects the 3
most common STIs. An ideal kit to discreetly test from the
comfort and privacy of your own home. CVS chlamydia test.
Gonorrhea Test Online
- Measures chlamydia, gonorrhea, & trich
- Urine sample collection
best at-home std test - best way to test for gonorrhea
$99.00
5 STD Check
Great for Quarterly Testing
Rapid Gonorrhea Test CVS
Great for Quarterly Testing
Rapid Gonorrhea Test CVS
At Home Standard STD Test (5-STIs)
Includes Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Trich + HIV, & Syphilis
Gonorrhea Rapid Test CVS
Check for 5 of the most common sexually transmitted infections across both sexes with this confidential STD at home test kit. chlamydia test CVS
at home chlamydia test CVS
At Home Gonorrhea Test CVS
- Measures for chlamydia, gonorrhea, trich + HIV, & syphilis
- Urine sample collection
- Finger prick sample collection
rapid gonorrhea test cvs
$149.00
7 STD Check
Most Popular
At Home Gonorrhea Test Walgreens
Most Popular
11 STD Check
Best for Risky Lifestyle
Oral Gonorrhea Test
Best for Risky Lifestyle
Oral Gonorrhea Test
At Home Complete STD Test (11-STIs)
Includes Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Trich + HIV, Syphilis,
Hepatitis C, & Herpes 2 – Genital, Throat & Anal Collection
An ideal test for the early detection of STIs in men and
women who participate in anal or oral sex. Our STD full panel test checks our complete menu of STIs, including gonorrhea and chlamydia transmission to the anus or throat.
Oral Gonorrhea Test Kit
- Measures chlamydia, gonorrhea, trich, HIV, syphilis,
hepatitis C & herpes 2 - Elevate your STD check by including anal & throat
collection - Finger prick, urine & swab sample collection
$259.00
$99.00
$149.00
$189.00
3 STDcheck – Most Economical Best Home STD Test
$259.00

Digital Results
Usually within 2 to 5 days of your gonorrhea urine test arriving at the lab, receive secure electronic STD results on your device of choice.
Simple
Simple to understand results provide your current STI status.
Individualized
Your individualized report measures Gonorrhea in urine.
Useful Results
Hospital-grade results for visibility into your sexual health — get clarity on your GC STD status from the privacy of your own home.
How It Works

Order Your Test
Collect Your Sample

Fast, Accurate Results

Get Physician Support
Other Online STD Tests
$99.00
$149.00
$189.00
3 STDcheck – Most Economical Best Home STD Test
$259.00
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s included in the at-home gonorrhea test kit?
You’ll receive everything you need in order to self-collect your test specimen!
• Pre-paid shipping both ways
• Discreet packaging
• Easy to follow instructions
• An at-home urine gonorrhea test collection kit
• Return protective envelope to mail sample to the lab for testing
• Electronic passcode protected results available from your phone or computer
• Printable report to share with your doctor
• Help along the way if you need it
How accurate is a urine test for gonorrhea?
NAAT Gonorrhea Test
Urine tests for gonorrhea known as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), like this test, are highly accurate in detecting the presence of the gonorrhea bacteria. These tests have been extensively studied and have shown excellent sensitivity and specificity.
The sensitivity of a test refers to its ability to correctly identify individuals who have the infection (true positives), while specificity refers to its ability to correctly identify individuals who do not have the infection (true negatives).
NAAT gonorrhea tests have high sensitivity and specificity, typically ranging from 95% or higher.2 This means that they are very reliable in accurately detecting gonorrhea infections.
However, it’s important to note that no test is 100% perfect, and there is always a small possibility of false-positive or false-negative results. Factors such as the timing of the test (wait at least two weeks following exposure or treatment) and sample collection technique (follow sample collection instructions closely) most commonly can affect test sensitivity and specificity. For the most accurate negative results, we recommend you retest after 3 moths from your post treatment or possible exposure date to confirm your negative GC STD status. If there are any concerns about positive results, we recommend you consult with a healthcare professional and have your test repeated.
Where is my gonorrhea urine test performed?
Same Lab Test Offered by Physicians & Hospitals
4U Health tests meet national standards and are as accurate as services provided in a doctor’s office or hospital. We only work with the highest quality CLIA certified laboratories and health experts. Your at home gonorrhea test complies with state and federal regulations. And our clinicians provide medical oversight throughout the entire process.
How long does a gonorrhea test take?
Gonorrhea Test Results Time
With 4U Health’s at-home gonorrhea test, the process typically takes 2 to 3 days to complete after the lab receives your sample. To accommodate for potential repeat testing, we estimate that you will receive your urine gonorrhea test results within 2 to 5 days.
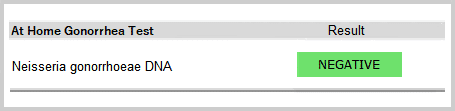
What does an at home gonorrhea test result show?
Gonorrhea Test Result
Your at home gonorrhea test results will tell you if your urine contains gonorrhea DNA. This test will confirm your GC STD status.
How soon after unprotected can I test for gonorrhea?
When To Test for Gonorrhea
Getting tested for gonorrhea after unprotected anal, vaginal, or oral sex is usually done no sooner than 2 weeks after potential exposure. For the most accurate results, some physicians recommend testing after 3 weeks. To attain complete peace of mind, you may consider a follow-up urine gonorrhea test at the 3-month mark to confirm your negative result and definitively rule out any possibility of a new GC STD infection.
How long will I test positive for gonorrhea after treatment?
When To Retest for Gonorrhea
The timing for retesting after completing a course of antibiotics to treat gonorrhea can vary depending on your medical history and the prescribed medication. Typically, it is recommended to wait at least two weeks after finishing the antibiotics before getting retested for a gonorrhea bacterial infection. This waiting period allows sufficient time for the antibiotics to clear the infection. However, some healthcare providers may advise waiting longer, such as three weeks, to ensure accurate GC STD results.
The CDC recommends urine gonorrhea testing at 3 months to confirm you cleared the infection and were not reinfected.1
Can I buy this gonorrhea urine test now and use it later?
Test now or within one year of purchase. This at home urine gonorrhea test kit has a guaranteed expiration date of at least 12 months. That’s great news if you are buying more than one test to recheck yourself in the future for a GC STD.
Can I gift this gonorrhea urine test to a friend or family member?
4U Health’s at home gonorrhea test is eligible for gifting. In fact, all 4U Health tests make great presents. The recipient who receives your gift will simply open the kit, register it, and follow the urine gonorrhea test collection instructions. Within a few days of sending to the lab, your significant other, friend or family member will receive secure electronic HIPAA compliant GC STD results all thanks to your generosity.
Will my at home gonorrhea test be covered by insurance?
Pay upfront and receive no surprise medical bills. Insurance carriers typically only cover an at home gonorrhea test once per year. 4U Health is not enrolled in Medicare or any other private insurance network. This gonorrhea urine test is not eligible for Medicare or any other federal or state-funded insurance program reimbursement. That’s great news if you want to test more than once a year or if you want to keep your GC STD testing experience confidential.
How is my privacy protected?
Rest assured; HIPAA security standards protect your data every step of the way while determining your gonorrhea status. Keeping your confidential data secure is our number one priority. We only share your information when required to deliver our products and services or where we are legally obligated to do so. Your results are securely protected and available for review in your online portal; always secure but easily accessible only to you.
Although protecting customer privacy is of utmost importance to us, similar to any STI testing process, including both 4U Health lab tests and those conducted by traditional in person healthcare providers, certain positive results are mandated by law to be reported to state health departments. This reporting is solely intended to monitor and track the prevalence of infections. If you receive positive test results for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Hepatitis C, Herpes Symplex 2, HIV, HPV, Syphilis, or Trichomoniasis through a 4U Health at-home STD test, depending on individual state requirements, our network of labs may share this information with your state health board for the purpose of tracking. Our at-home STD tests provide you with the knowledge of your STI status, and your information will remain otherwise confidential.
Common questions about gonorrhea symptoms
What are the symptoms of gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is known as a “silent” infection because it often does not cause noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, when symptoms do occur, they can vary depending on the affected area of the body. Common symptoms of gonorrhea may include:
Gonorrhea Symptoms Women
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Pain or a burning sensation during urination
- Painful periods or bleeding between periods
- Lower abdominal pain or pelvic pain
- Painful sexual intercourse
Gonorrhea Symptoms Male
- Clear or cloudy discharge from the penis
- Pain or a burning sensation during urination
- Testicular pain or swelling
- Itching or irritation at the opening of the penis
Oral Gonorrhea Symptoms
Oral gonorrhea, also known as pharyngeal gonorrhea, is a sexually transmitted infection that affects the throat. It is important to note that oral gonorrhea is typically asymptomatic, meaning it often does not cause noticeable symptoms. However, in some cases, oral GC STD may cause the following symptoms:
Sore throat: You may experience a persistent sore throat that is not alleviated with usual remedies.
Redness and inflammation: The back of your throat may appear red and swollen.
Difficulty swallowing: You may experience discomfort or pain when swallowing.
Tonsillitis-like symptoms: It is possible to experience symptoms similar to tonsillitis, such as swollen tonsils or white spots on the tonsils.
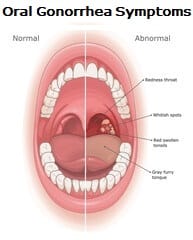
4U Health offers an at home gonorrhea test kit that in part checks for oral gonorrhea:
Full Panel STD Test (Complete-11)
Anal Gonorrhea Symptoms
Anal gonorrhea, also known as rectal gonorrhea, is a sexually transmitted infection that affects the rectum and anus. Similar to other forms of gonorrhea, anal gonorrhea can be asymptomatic, meaning it may not cause noticeable symptoms in some individuals. However, when rectal GC STD symptoms do occur, they can include:
Rectal pain: You may experience discomfort or pain in the rectal area.
Anal discharge: Some individuals may notice abnormal discharge from the anus.
Rectal bleeding: Bleeding from the rectum, particularly during bowel movements, may occur.
Itching or irritation: You may experience itching, irritation, or a feeling of fullness in the anal area.
Changes in bowel habits: Anal gonorrhea can sometimes lead to changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or constipation.
4U Health offers an at home gonorrhea test kit that in part checks for anal gonorrhea: Full Panel STD Test (Complete-11)
It’s important to note that symptoms of gonorrhea in women and men, along with oral and anal gonorrhea symptoms, can also be caused by other conditions and STIs. Moreover, some people infected with gonorrhea may not experience any symptoms at all. Regular testing is crucial, especially if you are sexually active or have had unprotected sex. If you suspect you may have gonorrhea or have been exposed to it, it is advisable to seek testing and when appropriate treatment.
Is rectal itching gonorrhea?
It can be, but not always. Gonorrhea can cause rectal itching. An itchy anus can be caused by various factors, and while some sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea can cause anal itching, it is not exclusive to STIs. There are several non-STI-related conditions that can lead to anal itching, including:
Poor hygiene: Insufficient cleaning of the anal area can result in irritation and itching.
Hemorrhoids: Swollen blood vessels in the rectal area can cause itching and discomfort.
Anal fissures: Small tears in the lining of the anus can cause itching and pain.
Yeast infections: Candida or other types of yeast infections can occur in the anal region and lead to itching.
Pinworms: A parasitic infection caused by pinworms can cause intense itching around the anus, especially at night.
Gonorrhea can be commonly spread by anal sex. Furthermore, anal itching can be associated with certain STIs such as chlamydia, genital herpes or genital warts. Howbeit, it is essential to remember that STIs are not the only possible cause. If you are experiencing anal itching or any other symptoms, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. You can also self-screen for anal STIs by ordering an at home rectal swab STD test with 4U Health.
Does gonorrhea cause vaginal itching?
Yes, but not always. Gonorrhea can cause vaginal itching. Several other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may also cause vaginal itching. Here are some common STIs that may lead to vaginal itching as a symptom:
Trichomoniasis: Trichomoniasis is caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. It can cause vaginal itching, along with other symptoms such as abnormal vaginal discharge (yellow-green, frothy, or foul-smelling), discomfort during urination, and vaginal redness.
Genital herpes: Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can cause genital herpes, which can result in itching, tingling, or a burning sensation in the genital area. This may be accompanied by the development of painful blisters or sores.
Chlamydia: Chlamydia is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. While chlamydia infection may not always cause noticeable symptoms, some individuals may experience vaginal itching or irritation, along with other symptoms such as abnormal vaginal discharge, pain during urination, or pain during sexual intercourse.
Gonorrhea: Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It can cause vaginal itching, along with symptoms like abnormal vaginal discharge, pain or burning during urination, and increased frequency of urination.
Vaginal Gonorrhea Symptoms
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea can cause various symptoms in the vaginal area. It’s important to note that not all STIs cause noticeable symptoms, and some infections may be asymptomatic. However, here are some common symptoms that may occur if an STI affects the vagina:
Abnormal vaginal discharge: Changes in vaginal discharge color, consistency, or odor. It may be white, yellow, green, gray, frothy, or have a foul smell.
Vaginal itching or irritation: Persistent itching or discomfort in the vaginal area.
Pain or discomfort during urination: A burning sensation or pain while urinating.
Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse: Pain or discomfort during or after sexual activity.
Vaginal bleeding: Unusual vaginal bleeding, such as between periods or after sexual intercourse.
Swelling or redness: Swelling, redness, or inflammation of the vaginal area.
Pelvic pain: Persistent pain or discomfort in the pelvic region.
It’s important to note that vaginal itching and other symptoms in the vaginal area can have various causes, including non-STI-related factors such as yeast infections (e.g., candidiasis) or allergic reactions.
What does gonorrhea in the throat look like?
Gonorrhea can cause symptoms in the throat, especially if transmitted through oral sex. However, it’s worth noting that not all gonorrhea throat infections result in noticeable symptoms, and some infections may not show any signs. Nevertheless, here are common symptoms that may arise if gonorrhea affects the throat.
Gonorrhea in Throat Symptoms
Sore throat: Persistent or recurring discomfort in the throat.
Difficulty swallowing: Pain or challenges when swallowing food or liquids.
Redness or inflammation: The throat may appear swollen, red, or inflamed.
Tonsillitis: Infection or inflammation of the tonsils, leading to soreness and swelling.
White patches or spots: Presence of white patches, spots, or lesions on the throat or tonsils.
Hoarseness or voice changes: Changes in the voice, such as hoarseness or a raspy voice.
Coughing or mucus production: Frequent coughing or the coughing up of mucus.
It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also be caused by various other conditions, not solely gonorrhea. If you suspect exposure to an STI through oral sex or experience any of these symptoms, you can get a throat swab STD test online at 4UHealth.
Does gonorrhea cause fever?
Yes, gonorrhea can cause fever as one of its potential symptoms. While not everyone with gonorrhea experiences fever, it is possible to develop an elevated body temperature as a result of the infection. Fever is generally considered a systemic response to an infection and can occur alongside other symptoms such as pain or discomfort during urination, abnormal genital discharge, and increased frequency of urination. If you suspect you may have gonorrhea or are experiencing symptoms, it is advisable to seek testing and treatment if necessary.
When do gonorrhea symptoms start?
The time when gonorrhea symptoms start can differ based on the specific location of your infection and other individual factors. In certain cases, symptoms may arise within weeks after exposure to an infected person, while in other situations, it may take months for gonorrhea symptoms to develop, or a person may not experience any GC STD symptoms at all.
Gonorrhea Timeline
Gonorrhea symptoms may appear within 2 weeks after exposure, although many individuals may not experience any symptoms.
It’s crucial to understand that the presence or absence of symptoms does not definitively indicate the presence of a gonorrhea infection. Regular testing and practicing safe sex are vital for early detection, appropriate treatment, and prevention of further transmission. If there is a suspicion of exposure to gonorrhea, it is advised you consult a healthcare provider or undergo a self GC STD check with an at home gonorrhea test kit.
More questions about gonorrhea
What is the clap STD?
“The clap” is a colloquial term used to refer to the sexually transmitted infection (STI) known as gonorrhea. Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium neisseria gonorrhoeae and can be transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person. It commonly affects the urethra, rectum, and throat, but can also infect other areas of the body.
The nickname “the clap” originated from an old French word, “clapier,” meaning brothel. It is believed to have been used in reference to the painful clapping motion that some men would make when seeking treatment for the infection. However, it’s important to note that using colloquial terms like “the clap” can lead to confusion and misunderstandings, so it is advisable to use the proper medical term, gonorrhea, when discussing the infection. If you suspect you may have gonorrhea or any other STI, it is recommended to seek testing and appropriate treatment when necessary.
Where can I get a rapid gonorrhea test?
You can get a rapid gonorrhea test at 4U Health, an online service that offers convenient and confidential at-home gonorrhea testing for men and women. For added convenience, 4U Health offers FedEx overnight shipping options for both delivering the test kit to your home and returning the sample to the laboratory. With 4U Health’s rapid gonorrhea test kit, you can receive your results within 2 to 5 days from the moment your sample arrives at the lab, ensuring a quick turnaround time.
Can you test urine for gonorrhea?
Yes, both men and women can test for gonorrhea using a urine sample. Urine tests are a common and convenient method for detecting gonorrhea infections, as they can accurately detect the presence of neisseria gonorrhea bacteria in the urinary tract.
How to test for gonorrhea?
Urine NAAT Gonorrhea Test
A nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) is the most common and accurate method for gonorrhea testing. It often involves collecting a urine sample from women or men. The urine gonorrhea sample, whether collected at home or at the doctor’s office, is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where it is checked for the presence of gonorrhea DNA. 4U Health offers an accurate at home gonorrhea test for men and women with detection of gonorrhea DNA. This is the same test method employed by physicians and hospitals.
Swab NAAT Gonorrhea Test
Swabs are taken from the throat, anus, penis, or vagina to evaluate for gonorrhea in individuals who partake in oral, anal and conventional vaginal sex. 4U Health offers an at home gonorrhea test kit that in part checks for anal and throat chlamydia by swab: Full Panel STD Test (Complete-11)
How do they test for gonorrhea female?
To test for gonorrhea in females, there are a few common methods:
Urine Test: This is the most convenient method for testing gonorrhea in females. You will be provided with a sterile container to collect a urine sample. It’s important to follow the instructions provided with your test for proper urine collection. 4U Health offers gonorrhea testing in females by urine.
Cervical Swab: A healthcare professional will gently collect a swab sample from the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that extends into the vagina. The swab is inserted into the vagina and rotated to collect cells from the cervix. This sample is then sent to a laboratory for testing.
Vaginal Swab: Some testing services may offer self-swab tests for females. In this method, you will be provided with a swab and instructions on how to collect a vaginal swab yourself. The swab is then sent to a laboratory for testing.
How do they test for gonorrhea male?
To test for gonorrhea in males, there are a few common methods:
Urine Test: This is the most convenient method for testing gonorrhea in males. You will be provided with a sterile container to collect a urine sample. It’s important to follow the instructions provided with your test or testing facility for proper urine collection. 4U Health offers gonorrhea testing in males by urine.
Urethral Swab: In some cases, a healthcare professional may recommend a urethral swab. They will insert a small swab into the opening of the urethra (the tube through which men pass urine) to collect a sample. This method may be uncomfortable but is generally quick and straightforward.
Where to get tested for gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea Test Near Me
Order a home gonorrhea test kit: You have the option to order an at home gonorrhea test online. Various providers, such as 4U Health, offer these tests. One example is the At Home Gonorrhea Test (GC STD), which is an easy urine test that is eligible for HSA/FSA reimbursement. Visit 4U Health’s STD product page to see the expansive selection of 17 STD test options.
Visit a local health clinic: You can seek assistance from a healthcare provider at an STD clinic near your location. They can evaluate your symptoms and conduct gonorrhea testing.
Explore retail stores offering home STD tests: Some retail stores like pharmacies carry kits often referred to by names like at home gonorrhea test Walgreens, at home gonorrhea test Walmart and CVS gonorrhea test, among others. You can check on their shelves for available specific brand name options.
Rapid Chlamydia Test
To obtain the 4U Health rapid gonorrhea test kit, you can conveniently order it online, with free shipping provided, and get quick results within 2 to 5 days of your sample arriving at the lab.
How to test for gonorrhea?
Testing for gonorrhea typically involves one of the following methods:
NAAT Gonorrhea Test
This is the most common and reliable method for gonorrhea testing. It involves collecting a sample from the affected area, such as the urethra in males or the cervix in females. The sample can be obtained through a swab or urine sample. The collected sample is then sent to a laboratory, where it is tested for the presence of gonorrhea DNA or RNA.
Rapid Gonorrhea Test Kit
Some clinics or healthcare facilities offer rapid tests that provide results within a short period, usually within 20 minutes. These tests may use swabs or urine samples, and they typically detect gonorrhea antigens. However, compared to NAAT, rapid antigen tests generally have lower sensitivity and specificity. This means that they may not detect gonorrhea infections as accurately as NAATs, and there is a higher chance of false-negative or false-positive results with rapid antigen tests.
4uhealth.com offers convenient online access to 17 at-home STD test kits, including options that screen for gonorrhea infections by NAAT. An at home STI test is a lab testing kit that allows individuals to test themselves for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in the comfort and privacy of their own homes. 4U Health’s home STD kits include instructions, collection materials (such blood, swab, or urine collection devices), and prepaid packaging for returning the samples to a laboratory. Once the samples are sent back, they are analyzed by a CLIA certified laboratory, and the individual receives their secure digital test results confidentially. 4U Health’s at-home STD tests provide a convenient and discreet option for individuals to monitor their sexual health and seek appropriate medical care if needed.
How to get a gonorrhea test?
You can conveniently purchase an at home gonorrhea test kit from 4uhealth. We recommend you view our STD product category page to view our expansive selection of 17 blood, urine and swab STD test kits. Select the specific urine STD test, blood STD test or STD panel that meets your unique needs. After placing your order for an at-home STI test, your kit will be delivered discreetly to your door, ensuring utmost privacy and convenience in obtaining your STD status.
How does a gonorrhea test work?
A gonorrhea test works by detecting the presence of this bacterial infection in an individual’s body. Common methods include urine tests and swab tests of the affected area. Depending on the type of test, the lab aims to identify the genetic material, antibodies, or antigens associated with gonorrhea. The collected biological samples are sent to a laboratory where trained professionals analyze them using specialized techniques. 4U Health offers confidential gonorrhea results delivered securely to your device of choice.
With 4U Health, you have the option to conveniently get an at-home gonorrhea test kit. Also referred to as an at-home STI test, this type of testing kit allows individuals to collect their own samples in the comfort and privacy of their own homes. The home gonorrhea kit includes detailed instructions, collection materials, and prepaid packaging for returning the samples to a certified laboratory. Once the samples arrive at the lab, 4U Health offers secure digital results usually within 2 to 5 days. At-home STD testing provides a discreet and convenient alternative to traditional clinic visits, empowering individuals to take control of their sexual health with privacy and ease.
How much is a gonorrhea test
Many people looking to take a STI gonorrhea check for the first time often ask how much is a gonorrhea test kit. 4U Health offers many confidential at home STD tests with blood, swab, or urine sample collection for the affordable price of fifty-nine Dollars thru two hundred fifty-nine Dollars. ($59 – $259). All tests include free shipping both to your home and back to the lab. All at home gonorrhea test kits offer all the supplies necessary to collect your swab gonorrhea test or urine gonorrhea test. See 4U Health’s expansive catalogue of home STD test kits to find the best option for your unique needs.
What is the difference between gonorrhea and chlamydia?
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are both sexually transmitted infections (STIs) caused by different bacteria, Neisseria gonorrhoeae for gonorrhea and Chlamydia trachomatis for chlamydia. While they are distinct infections, there are some similarities and differences between the two:
Causative Organisms: Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, while chlamydia is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
Symptoms: Both gonorrhea and chlamydia can be asymptomatic, meaning they may not cause noticeable symptoms in some individuals. However, when symptoms do occur, they are hard to differentiate. Gonorrhea and chlamydia can both cause symptoms such as abnormal genital discharge, painful urination, and pain during sexual intercourse. It’s important to note that both infections can also lead to complications if left untreated.
Complications: If untreated, both gonorrhea and chlamydia can result in serious complications. In females, untreated gonorrhea and chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause infertility and chronic pelvic pain. In males, complications can include epididymitis (inflammation of a tube at the back of your testicle that carries sperm) and infertility. Both infections can also increase the risk of contracting or transmitting HIV.
Testing: Testing methods for gonorrhea and chlamydia are similar and often performed together. They can involve nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) using samples collected from the affected area, such as urine or swab samples.
Treatment: Both gonorrhea and chlamydia are typically treated with antibiotics. However, antibiotic resistance has become a concern for both infections, particularly for gonorrhea.
If you suspect you may have either infection or have concerns about potential exposure, it is advisable to seek testing and appropriate treatment when necessary.
How to test for chlamydia and gonorrhea?
To test for chlamydia and gonorrhea, you can consider ordering an STD panel from 4U Health, a trusted online lab test provider. 4U Health’s Essential-3 STD Test allows for comprehensive testing of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis, the three most common STIs in both males and females. The is a simple and convenient at home urine STD test option.
Does trichomoniasis show up on a gonorrhea test?
Trichomoniasis, caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, does not show up on a standard gonorrhea test. Gonorrhea and trichomoniasis are two separate sexually transmitted infections (STIs) caused by different organisms and require different tests for detection.
If you suspect you may have trichomoniasis or want to test for multiple STIs including chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis, you can consider ordering an STI panel that includes tests for these specific infections. 4U Health’s Essential-3 STD Panel is a testing option that checks for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis, providing a comprehensive assessment of these common STIs.
Does pap smear test for gonorrhea?
No, a Pap smear does not test for gonorrhea. A Pap smear is a screening test used to detect abnormal changes in the cells of the cervix that could indicate cervical cancer or pre-cancerous conditions. It involves collecting cells from the cervix and examining them under a microscope. Gonorrhea testing requires a separate specific test, such as a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT), which detects the presence of the gonorrhea bacteria. If you are concerned about gonorrhea, it is important to request a separate gonorrhea test in addition to a Pap smear. You can get an at home chlamydia test online at 4U Health.
How long does it take for gonorrhea to show up on a test?
Gonorrhea can usually be detected through testing within 2 to 5 days after exposure with a NAAT test like the kind 4U Health offers. However, it’s important to note that the timing can vary depending on several factors, and it may take up to 3 weeks for the gonorrhea infection to reach a detectable level. We recommend not testing before two weeks from your suspected exposure date.
False Negative Gonorrhea Test
There are several reasons why a gonorrhea test may yield a false negative result, meaning it incorrectly indicates the absence of gonorrhea infection. Some common reasons for false negative gonorrhea results include:
Timing of the test: Gonorrhea infections can take time to reach detectable levels in the body. If a test is performed too soon after exposure or infection, the amount of gonorrhea bacteria in the sample may be below the test’s detection threshold, resulting in a false negative result. It is recommended to wait at least 2 weeks after exposure or to follow the specific testing guidelines provided by the healthcare professional or testing facility.
Incorrect sample collection: Improper collection of the sample can lead to inaccurate results. If the sample is not collected correctly, it may not contain sufficient amounts of gonorrhea bacteria for detection. It is important to carefully follow the instructions provided with the test kit or seek assistance from a healthcare professional to ensure proper sample collection.
Laboratory errors: Errors can occur during the laboratory processing of the samples, leading to false negative results. While rare, mishandling, contamination, or technical issues in the laboratory can affect the accuracy of the test.
If a person experiences persistent symptoms or has concerns about a possible gonorrhea infection despite a negative test result, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation. They can provide appropriate guidance and recommend additional testing or treatment options if necessary.
False Positive Gonorrhea Test
While false positive results for gonorrhea tests are relatively rare, they can still occur. Some potential reasons for false positive gonorrhea test results include:
Laboratory errors: Mistakes or contamination during sample processing or testing in the laboratory can lead to false positive results. Although laboratories have strict quality control measures in place, human error or technical issues can occasionally occur.
Cross-reactivity: Gonorrhea tests rely on specific antigens or genetic material associated with the gonorrhea bacteria. In rare cases, the test may cross-react with other bacteria or substances present in the sample, leading to a false positive result. This is more common with older or less specific testing methods not sold by 4U Health.
Previous infection or treatment: If a person has previously been infected with gonorrhea and has completed treatment, traces of the bacteria may still be present in the body. This can lead to a positive test result even though the person is no longer actively infected.
Non-gonococcal urethritis: Other conditions, such as urinary tract infections or certain sexually transmitted infections like Mycoplasma genitalium or Ureaplasma urealyticum, can cause similar symptoms to gonorrhea. These conditions can sometimes result in a false positive gonorrhea test.
Contamination of the sample: Improper sample collection or contamination during collection can introduce external bacteria or substances that may interfere with the test, potentially leading to a false positive result.
If a gonorrhea test comes back positive, it is generally recommended to confirm the result with additional testing or to seek medical advice for further evaluation and appropriate treatment. A healthcare professional can provide guidance and conduct further tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Can you test negative for gonorrhea and still have it?
Yes, it is possible to test negative for gonorrhea and still have the infection. This can occur due to several reasons. First, the timing of the test plays a role as the infection may not have had enough time to replicate and reach detectable levels at the time of testing. Second, false-negative results can also occur due to errors in sample collection, handling, or laboratory testing procedures. Lastly, gonorrhea can enter a dormant or persistent state in the body where it is present but not actively causing symptoms or showing up on certain types of tests. If you have persistent symptoms or ongoing concerns, it is important to discuss with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and possibly retesting.
Can gonorrhea be dormant and test negative?
Yes, it is possible for gonorrhea to be dormant in the body and not show up on a certain types of gonorrhea tests, resulting in a false-negative result. Gonorrhea can sometimes enter a dormant or persistent state where the bacteria remain in the body but do not cause noticeable symptoms or show up on standard diagnostic tests.
During the dormant phase, the gonorrhea bacteria can still be present in the body and potentially transmitted to others. This is why regular testing is important, especially for individuals who are sexually active or have engaged in high-risk sexual behaviors.
To increase the accuracy of gonorrhea testing, it is recommended to wait at least two weeks after a potential exposure before getting tested. This allows enough time for the bacteria to replicate and become detectable in diagnostic tests. We recommend and only offer nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) for gonorrhea . These are highly sensitive and specific for detecting gonorrhea infections, including dormant or persistent gonorrhea. NAATs are designed to target specific genetic material of the gonorrhea bacteria, allowing for accurate detection even during the dormant phase. If you are ever concerned about a false negative test, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation or retest at 3 months to confirm your negative result.
Can a UTI cause a false positive gonorrhea test?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are not known to cause false positive results on nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) used for gonorrhea testing, the methodology employed by 4U Health. NAATs are highly specific for detecting the genetic material of neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacteria that causes gonorrhea. UTIs are typically caused by different bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) or other pathogens, and do not contain the genetic material specific to gonorrhea.
It’s important to note that if a person has both gonorrhea and a UTI simultaneously, the presence of a UTI should not interfere with the accuracy of a gonorrhea test. NAATs are designed to specifically detect gonorrhea and are not influenced by the presence of other infections.
If you have concerns about the accuracy of your gonorrhea test results or suspect a possible UTI, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your symptoms, order appropriate tests, and provide proper diagnosis and treatment.
If you have gonorrhea will you test positive for a UTI?
No, having gonorrhea does not necessarily mean that you will test positive for a urinary tract infection (UTI). Gonorrhea and UTIs are two distinct types of infections that are caused by different organisms.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium neisseria gonorrhoeae. It primarily affects the reproductive organs and can also infect the throat and rectum. Testing for gonorrhea requires specific tests, such as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), that detect the presence of the gonorrhea bacteria.
On the other hand, a UTI typically refers to an infection in the urinary tract, including the bladder, urethra, or kidneys. Common symptoms of a UTI include frequent urination, pain or burning sensation during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and lower abdominal pain. UTIs are usually caused by bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), which are different from the bacteria that cause gonorrhea. However, many of the symptoms of a UTI overlap with symptoms of gonorrhea.
While it is possible to have both gonorrhea and a UTI simultaneously, testing positive for gonorrhea does not automatically indicate the presence of a UTI. If you suspect you may have a UTI or gonorrhea , it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can recommend the appropriate tests and provide the necessary treatment based on your symptoms and medical history.
You can get an at gonorrhea test online at 4U Health. Starting in the 3rd quarter of 2023, 4U Health plans to release a convenient at home UTI test kit.
Can you get gonorrhea from oral sex?
Indeed, engaging in oral sex is a form of sexual contact that can elevate the chances of acquiring gonorrhea. Gonorrhea can be transmitted when there is direct contact between the mouth, throat, or tongue of one person and the genitals of an infected person. This includes performing oral sex on an infected partner or receiving oral sex from an infected partner.
It’s worth noting that gonorrhea infections can occur in the throat and cause oral gonorrhea . However, it’s also possible for gonorrhea to spread from the throat to the genitals through subsequent sexual activities, such as vaginal or anal sex.
Using barrier methods, such as dental dams or condoms, during oral sex can reduce the risk of transmitting or contracting gonorrhea. Regular testing for sexually transmitted infections, including gonorrhea, is important, especially for individuals who engage in oral sex or have multiple sexual partners. If you suspect you may have gonorrhea or have concerns about potential exposure, it is advisable to seek testing and if necessary treatment.
How to test for oral gonorrhea?
To test for oral gonorrhea, it is recommended to order a Pull Panel STD Test that includes oral gonorrhea testing. 4U Health offers a comprehensive STD testing option called the Complete-11 panel, which covers a wide range of sexually transmitted infections, including oral chlamydia and gonorrhea. Simply order the test online, collect the required oral sample following the provided instructions, and return it to the laboratory for analysis. Within a few days, you’ll receive your secure digital results, allowing you to access them conveniently and take appropriate actions if necessary.
Can you get gonorrhea from anal sex?
Yes, engaging in anal sex can potentially transmit gonorrhea. Anal intercourse carries a higher risk of transmitting certain STIs compared to other forms of sexual activity. This is because the anal tissue is delicate and can be more susceptible to tearing or injury, providing an entry point for infections. Gonorrhea and these other common STIs that can be transmitted through anal sex:
Chlamydia: Chlamydia trachomatis, the bacterium responsible for chlamydia, can infect the rectum during anal sex. Symptoms may include rectal pain, discharge, or bleeding.
HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can be transmitted through anal sex, as the rectal lining can be easily damaged during intercourse, allowing for the entry of the virus.
Gonorrhea: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacteria that cause gonorrhea, can be transmitted through anal sex if one partner is infected. The bacteria can infect the rectum and cause symptoms such as anal discharge, pain, or itching.
Syphilis: Treponema pallidum, the bacterium that causes syphilis, can be transmitted through anal sex. Syphilis can cause sores or ulcers in the anal area.
Herpes: Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can be transmitted through anal sex, leading to the development of painful blisters or sores around the anus or rectum.
Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) can be transmitted through anal sex, especially if there is contact with infected blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. The primary mode of HCV transmission is through direct blood-to-blood contact, so any sexual activity that involves the exchange of blood or the potential for bleeding increases the risk of transmission.
It’s important to note that using barrier methods such as condoms during anal sex can significantly reduce the risk of STI transmission. Regular testing, open communication with sexual partners, and practicing safe sex are essential for preventing and managing STIs. If you engage in anal sex and have concerns about STIs, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or perform a self STD check. 4U Health offers a rectal swab at home STD test.
How to test for rectal gonorrhea?
To test for rectal gonorrhea, it is recommended to order a Pull Panel STD Test that includes anal gonorrhea testing. 4U Health offers a comprehensive STD testing option called the Complete-11 panel, which covers a wide range of sexually transmitted infections, including rectal chlamydia and gonorrhea. Simply order the test online, collect the required rectal sample following the provided instructions, and return it to the laboratory for analysis. Within a few days, you’ll receive your secure digital results, allowing you to access them conveniently and take appropriate actions if necessary.
How likely is it to get gonorrhea with a condom?
When used correctly and consistently, condoms are estimated to provide a high level of protection against chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), but it is important to note that no method of protection is 100% effective. Condoms act as a barrier, preventing the exchange of bodily fluids that can transmit the infection. While condoms provide a high level of protection, they are not foolproof, and there is still a small chance of gonorrhea fluid transmission due to factors such as condom breakage or slippage. Also, please keep in mind oral sex without a condom can cause transmission of chlamydia between partners.
To ensure your sexual health and obtain peace of mind, it is recommended to consider regular testing for gonorrhea, especially if you are sexually active or have had a recent high-risk encounter. 4U Health offers convenient and confidential at-home gonorrhea testing options.
How often should you get tested for gonorrhea?
The frequency of testing for gonorrhea depends on individual risk factors and sexual behavior. It is generally recommended to get tested for chlamydia annually or more frequently if you engage in high-risk sexual activities. Here are some guidelines for gonorrhea testing:
Annual Testing: If you are sexually active and have no specific risk factors, it is recommended to get tested for gonorrhea at least once a year. This regular testing helps detect any potential infections early and ensures prompt treatment.
New Sexual Partner: Whenever you start a new sexual relationship or have multiple sexual partners, it is advisable to get tested for chlamydia as part of a comprehensive sexual health check-up. This can help identify and treat any existing infections and prevent the spread of chlamydia.
Symptomatic Individuals: If you experience symptoms such as unusual vaginal or penile discharge, pain or discomfort during urination, or pelvic pain, it is crucial to get tested for gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted infections promptly.
Retesting After Treatment: If you have been diagnosed and treated for gonorrhea, it is recommended to get retested approximately three months after completing treatment. This ensures that the infection has been successfully cleared and helps to rule out any potential reinfection.
High-Risk Sexual Activity: In high-risk individuals, it is recommended to consider monthly to quarterly chlamydia testing, depending on your unique circumstances.
Remember, these are general guidelines, and it is best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on your specific circumstances and sexual behavior.
Risky Sex
In high-risk individuals, it is recommended to consider quarterly gonorrhea testing. “High risk” typically refers to individuals who engage in behaviors or have certain characteristics that increase their chances of acquiring gonorrhea or other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). High-risk individuals may include:
Multiple Sexual Partners: Having multiple sexual partners increases the likelihood of exposure to gonorrhea and other STIs. Individuals who engage in casual or unprotected sexual encounters with multiple partners are considered high risk.
Recent STI History: If you have previously tested positive for gonorrhea or other STIs, you may be at higher risk of reinfection. Regular testing, including quarterly gonorrhea testing, can help detect any recurrent infections.
Unprotected Sex: Engaging in sexual activities without using barrier methods, such as condoms or dental dams, increases the risk of contracting gonorrhea. Unprotected sex includes vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse without the use of appropriate protection.
Sex with High-Risk Partners: Sexual partners who have a history of STIs, engage in high-risk behaviors, or have multiple sexual partners themselves can increase your risk of gonorrhea transmission.
Sex Workers or Individuals in Sexually Active Professions: Individuals working in the sex industry or occupations with higher rates of sexual activity may have an increased risk of gonorrhea and should consider regular testing.
It’s important to note that these are general examples, and the determination of high risk should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional who can assess your specific situation.
How to treat gonorrhea ?
Curious about self-treating gonorrhea at home? Due to the potential risks associated with untreated or improperly treated STIs, it is strongly advised not to attempt self-treatment. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to explore suitable antibiotic treatment options if you test positive for gonorrhea.
How to treat gonorrhea at home?
While it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of gonorrhea, there are a few general measures you can take at home to alleviate symptoms or promote overall comfort:
Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help relieve pain, fever, or inflammation associated with certain gonorrhea symptoms. Follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult a pharmacist if you have any concerns or are taking other medications.
Warm compress: Applying a warm compress or taking warm baths can help soothe discomfort caused by genital sores or inflammation.
Hygiene practices: Maintain good hygiene by gently cleaning the affected area with mild soap and water. Avoid harsh soaps or douching, as they can further irritate the area.
Avoid sexual activity: Refrain from sexual activity until you receive appropriate medical treatment and clearance from a healthcare professional to prevent further transmission or complications.
However, it is important to emphasize that self-treatment or home remedies may not effectively address the underlying infection or provide complete relief. It is strongly recommended to seek professional medical advice, diagnosis, and treatment from a healthcare provider who can provide appropriate care tailored to your specific situation. They can prescribe antibiotics, or other necessary treatments based on your specific needs.
How long after antibiotics to retest for gonorrhea?
Test of Cure Gonorrhea
The timing for retesting for gonorrhea after completing a course of antibiotics can vary depending on several factors, including the specific treatment provided. It’s important to follow the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they can provide you with personalized recommendations based on your specific situation. In general, it is typically recommended to wait at least two weeks after completing the antibiotics before getting retested. This allows enough time for the antibiotics to clear the gonorrhea infection. However, some healthcare providers may recommend waiting longer, such as three weeks, to ensure accurate results. The CDC recommends testing at 3 months post gonorrhea treatment to ensure against reinfection.
How do doctors test for gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea STD Tests
Doctors typically test for gonorrhea by using one of the following methods:
Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs): This is the most common and highly accurate testing method for gonorrhea. It involves collecting a sample of cells or fluids from the affected area, such as urine, swabbing the urethra in men or cervix in women, or swabbing the throat or rectum if those areas are potentially affected. The sample is then analyzed in a laboratory to detect the presence of gonorrhea DNA or RNA. 4U Health employs this testing method for all of its gonorrhea home test kits.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): ELISA tests detect the presence of gonorrhea-specific antibodies. These tests are less commonly used than NAATs but may be utilized in certain situations, such as when rapid results are needed.
What are the most common STDs in the US?
Most Common STDs
1 in 5 peaople in the US have a STD. In 2018 alone, approximately 26 million Americans had a sexually transmitted disease (STD). The specific ranking and infection rates of STDs vary over time. It’s always best to refer to up-to-date sources such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for the most recent information. Incidence of STDs means new infections. Here is a list of common STDs in rough order of incidence as of 2018:
1. Human papillomavirus (HPV): 13 million (M) estimated new HPV infections.
2. Trichomoniasis (Trich): 6.9 M estimated new Trich infections.
3. Chlamydia: 4 M estimated new Chlamydia infections.
4. Gonorrhea: 1.6 M estimated new Gonorrhea infections.
5. Herpes Symplex 2 (HSV-2): 572,000 estimated new HSV-2 infections.
6. Syphilis: 146,000 estimated new syphilis infections in 2018.
9. Hepatitis C (HCV): 50,000 estimated new HCV infections1 in 2018.
7. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): 33,000 estimated new HIV infections in 2018.
8. Hepatitis B (HBV): 8,300 estimated new HBV infections in 2018.
What are the common STDs?
What is Human Papillomavirus (HPV)?
HPV, or Human Papillomavirus, is a common viral infection that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. There are various strains of HPV, some of which can cause genital warts and increase the risk of certain types of cancer, such as cervical, anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, or oropharyngeal cancer. There is no cure for HPV. While most HPV infections resolve on their own without causing symptoms or complications, vaccination, regular screenings, and practicing safe sex are important preventive measures to reduce the risk of HPV-related health issues.
What is what is Trichomoniasis (Trich)?
Trich is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. It is a common STI that affects both men and women, but it is more common in women. Trichomoniasis is transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, oral, and anal sex. Most people with trichomoniasis do not experience any symptoms, but if symptoms do occur, they can include itching or irritation in the genital area, discharge from the vagina or penis (which may be frothy and yellow-green), pain or burning during urination, and pain during sexual intercourse. Trichomoniasis is usually treated with antibiotics, and it is important to get tested and treated if you are sexually active or have had unprotected sex with a new or casual partner. Using condoms and other forms of protection can help reduce the risk of trichomoniasis and other STIs.
What is Chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is one of the most common STIs in the world and can affect both men and women. Chlamydia is transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, oral, and anal sex. It can also be transmitted from a mother to her baby during childbirth. Most people with chlamydia do not experience any symptoms, but if left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems, such as infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease. Chlamydia is usually treated with antibiotics, and it is important to get tested and treated if you are sexually active or have had unprotected sex with a new or casual partner. Using condoms and other forms of protection can help reduce the risk of chlamydia and other STIs.
What is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is a common STI that can affect both men and women. Gonorrhea is transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, oral, and anal sex. It can also be transmitted from a mother to her baby during childbirth. Most people with gonorrhea do not experience any symptoms, but if left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems, such as infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease. Gonorrhea is usually treated with antibiotics, and it is important to get tested and treated if you are sexually active or have had unprotected sex with a new or casual partner. Using condoms and other forms of protection can help reduce the risk of gonorrhea and other STIs.
What is genital Herpes?
Genital Herpes is a viral infection generally caused by the Herpes simplex 2 virus (HSV2). It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. The infection results in the development of painful sores or blisters in the genital area. These sores can recur periodically and may be accompanied by flu-like symptoms such as fever and swollen lymph nodes. While there is no cure for genital Herpes, antiviral medications can help manage outbreaks, reduce symptoms, and decrease the risk of transmission. It is important to practice safe sex and communicate openly with sexual partners to minimize the risk of contracting or spreading genital Herpes.
Herpes 1 or 2 which is worse?
In terms of severity, both Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2) can cause similar symptoms, but HSV-2 is generally associated with more frequent and severe outbreaks of genital Herpes. However, it’s important to note that individual experiences with the virus can vary, and the impact of the infection can be influenced by factors such as the person’s immune system and management of the condition.
What is Syphilis?
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Syphilis progresses through different stages, including primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary stages, each with its own set of symptoms and complications. It can present as painless sores or ulcers, rash, fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. Syphilis can have severe long-term consequences if left untreated, affecting various organs and systems in the body, including the heart, brain, and nervous system. Early detection through testing and prompt treatment with antibiotics can effectively cure Syphilis and prevent its complications.
What is Hepatitis C (HCV)?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It is caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is commonly transmitted through contact with infected blood, such as through sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia, receiving contaminated blood transfusions, from mother to baby during childbirth, or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C can lead to both acute and chronic liver disease, and if left untreated, it can cause severe complications like liver cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Treatment options for hepatitis C have improved in recent years, and antiviral medications can effectively cure the infection in most cases, reducing the risk of long-term liver damage. It is important to get tested for hepatitis C if at risk and take preventive measures to avoid exposure.
What is Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)?
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. It is a viral infection that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, a type of white blood cell crucial for the body’s defense against infections. HIV is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing contaminated needles or syringes, and from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding. If left untreated, HIV can progress to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), which is the late stage of the infection and characterized by severe immune system damage, making individuals more susceptible to opportunistic infections and certain cancers. While there is no cure for HIV, antiretroviral therapy (ART) can effectively manage the virus, allowing people with HIV to live long and healthy lives. Preventive measures such as practicing safe sex, using sterile needles, and accessing HIV testing and treatment are crucial in reducing transmission rates and improving overall health outcomes.
What is Hepatitis B (HBV)?
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It is caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). The infection can be transmitted through contact with infected blood, unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia, and from mother to baby during childbirth. Hepatitis B can lead to both acute and chronic liver disease, which can range from mild illness to severe conditions such as liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. While there is no cure for Hepatitis B, antiviral medications and vaccines are available to manage the infection, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of transmission. It is important to get vaccinated against Hepatitis B and take precautions to avoid exposure to infected blood and other bodily fluids.
STD list of references
New England Journal of Medicine. Asymptomatic gonorrhea in men. URL. January 1, 1974. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. URL. Updated April 11, 2023. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines, 2021 – Adolescents. URL. Updated July 22, 2021. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Sentinel surveillance of rectal chlamydia and gonorrhea among males–San Francisco, 2005-2008. URL. January, 2010. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. Screening for STIs at Home or in the Clinic. URL. February 1, 2012. Accessed July 2, 2023.
New England Journal of Medicine. A trial of minocycline given after exposure to prevent gonorrhea. URL. May 10, 1979. Accessed July 2, 2023.
JAMA. Risk of acquiring gonorrhea and prevalence of abnormal adnexal findings among women recently exposed to gonorrhea. URL. December 16, 1983. Accessed July 2, 2023.
UpToDate. Prevention of sexually transmitted infections URL. Updated May 09, 2023. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Journal of American College Health. Rates of asymptomatic nonurethral gonorrhea and chlamydia in a population of university men who have sex with men. URL. 2012. Accessed July 2, 2023.
MedlinePlus. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. URL. Updated February 17, 2023. Accessed July 2, 2023.
AGS Health in Aging Foundation. Safe Sex for Older Adults . URL. Updated August 2019. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Nemours Foundation. Talking to Your Kids About STDs. URL. Updated July 2018. Accessed July 2, 2023.
American Academy of Pediatric. Medications for Sexually Transmitted Infections. URL. Updated November 21, 2015. Accessed July 2, 2023.
NHS. How soon do STI symptoms appear? URL. Updated 22 November 2019. Accessed July 2, 2023.
US Department of Health and Human Services. Your Rights Under HIPAA. URL. January 19, 2022. Accessed July 2, 2023.
University of Washington STD Prevention Training Center. National STD Curriculum. URL. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Infection Control Today. Sexually Transmitted Infections Increasingly Plague the United States. URL. November 10, 2022. Accessed July 2, 2023.
New York Times. Why Are Sexually Transmitted Infections Surging? URL. May 17, 2022. Accessed July 2, 2023.
National Coalition of STD Directors. Chlamydia, gonorrhoea & syphilis: STDs on the rise. URL. February 6, 2022. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases. What proportion of episodes of gonorrhoea and chlamydia becomes symptomatic?. URL. February 2002. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Lancet. Clinical spectrum of gonococcal infection in women. URL. June 4, 1977. Accessed July 2, 2023.
MedlinePlus: National Library of Medicine. Gonorrhea. URL. Updated December 6, 2021. Accessed July 2, 2023.
MedlinePlus: National Library of Medicine. Gonorrhea Test. URL. Updated December 3, 2020. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Obstetrics & Gynochology. Female gonorrhea: its relation to abnormal uterine bleeding, urinary tract symptoms, and cervicitis. URL. February 1975. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Annals of Internal Medicine. Anorectal gonococcal infection. URL. March 1977. Accessed July 2, 2023.
New England Journal of Medicine. Clinical spectrum of pharyngeal gonococcal infection. URL. January 25, 1973. Accessed July 2, 2023.
World Health Organization. Effectiveness of condoms in preventing sexually transmitted infections. URL. June 1, 2004. Accessed July 2, 2023.
Still have questions about the test?
So you still have unanswered questions. No worries, we’d love to hear from you. Reach us by e-mail, phone or chat and we will do our best to provide answers so you can determine if this is the best test for you or your partner.
- 866-610-1200
- help@4uhealth.com
- Chat Support
at home gonorrhea test CVS - PO Box 100083
Pittsburgh, PA 15233
